
The Emotet botnet now has a new module that steals credit card information stored in Google Chrome user profiles.
Emotet was first discovered by cybersecurity researchers at Proofpoint, who released the new module on June 6. It attempts to steal names, expiration dates, and card numbers stored in Chrome user profiles. An interesting detail is that the thief extracts the data to a different command and control (C2) server than the module loader.
Emotet has had enough of a trick. It was almost completely removed from the web a year ago when German authorities used their own infrastructure to provide a module that uninstalled the malware (opens in a new tab) from all infected devices.
emote is back
It returned six months later, in November 2021, when several cybersecurity researchers detected that Trickbot was trying to download a DLL, identified as Emotet, on the system.
A little over a month ago, Emotet operators were reported to be moving away from Microsoft Office macros for distribution and towards Windows Shortcut (.lnk) files.
The malware was first seen in the wild in 2014. At the time, it was used as a banking Trojan, but has since evolved into a botnet. Some researchers believe that it was developed by a threat actor known as Mummy Spider (AKA TA542) to act as a dropper for second-stage viruses. Among other things, Emotet was seen launching Qbot and Trickbot which, in turn, were seen delivering Cobalt Strike beacons and various strains of ransomware (opens in a new tab), including Ryuk or Conti.
Today, it is capable of stealing sensitive and personally identifiable data, spying on traffic passing through compromised networks, and moving laterally.
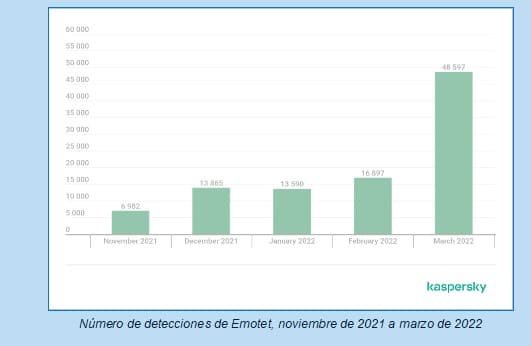
ESET cybersecurity researchers recently said that Emotet has seen a significant increase in activity this year, "with activity increasing more than 100 times compared to Q2021 XNUMX."
Via: BleepingComputer (Opens in a new tab)