
What is HFR?
Great frame rates are becoming more essential for average viewers, particularly sports or gaming enthusiasts, but, like many TV-related initials,
HFR can confuse anyone else who is not up to date.
In short, HFR is short for High Frame RateAnd you've probably heard the term in relation to the best TVs, next-gen game consoles, and even the new Apple TV 4K (2021). In general, frame rates increase, more
For what reason is this so essential? Let us give you some background on vital viewing metrics and what's changing in the world of HFR TVs today.
What is a frame rate?
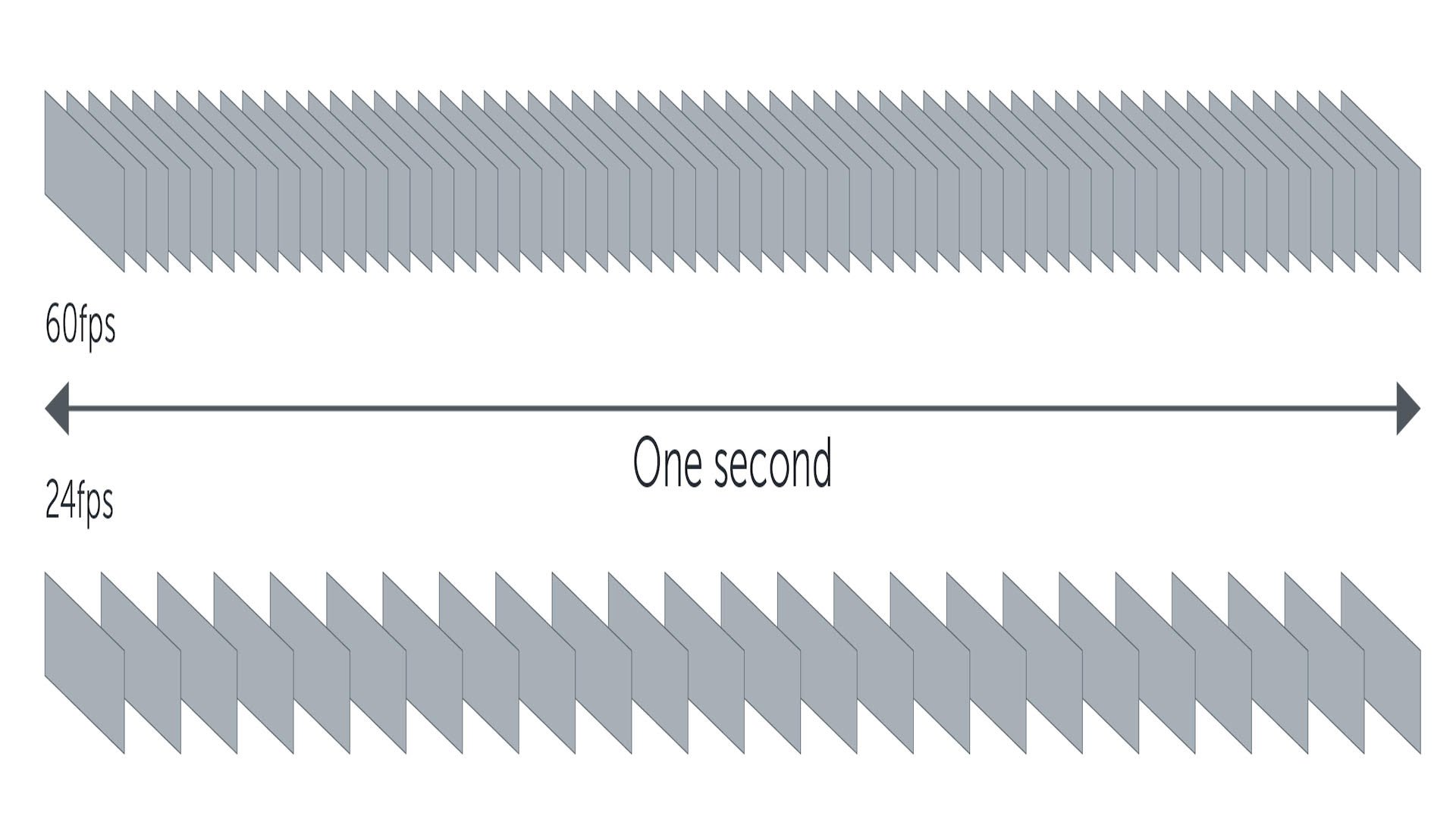
Any moving image is made up of a series of still images or images which, when read in rapid succession, are perceived by the brain as a moving image, of
hence the term "moving images".
The more frames per second (fps), the smoother and smoother the motion will be and the greater the level of detail that that moving frame can contain.
What frame rate is used in cinema?
In early cinema, frame rates changed from 16 to 26 fps, but the introduction of sound in the late 24s required a standard for matching the picture to the optical soundtrack. It was decided to use XNUMX frames per second,
primarily due to the fact that most theaters back then could handle that frame rate particularly, and has remained the rule of film production (impressively) for the last 100 years.
(Image credit: TechSmith
What is the frame rate of the TV?
When televisions were introduced to homes in the 1950s, the approach was slightly different. This is because standard definition broadcasts use a series of interlaced images that are displayed at a frequency of fifty or sixty Hz, depending on the TV standard used. The reason why these interlaced signals used a frequency of 50Hz or 60Hz was directly related to the nutrition source of that particular territory,
so in the United Kingdom and Europe it was PAL at 50Hz, while the USA and Japan used NTSC at 60Hz.
At that time, TV images were made up of a series of scan lines,
so an interlaced image essentially scanned half of the image and then the other half of the image at a refresh rate of fifty or sixty times per second. Because it happened so quickly, the brain would unconsciously combine these interlaced images into
a full field image at a rate of 25 or 30 frames per second.
As transmission and display technologies developed, TV production was able to use progressive scan video, which essentially means shooting at 25 or 30 full-field video frames per second, which is usually the case, called twenty-five fps for PAL and thirty fps for NTSC.
Since these 2 frame rates are very close to the XNUMX frames per second used in cinema, it was also partially simple to show movies on TV.

Apple TV 4K (two thousand twenty-one) adds support for HFR display (Image credit: Apple)
What is high frame rate (HFR)?
A high frame rate is simply a frame rate higher than the established 24, 25, or 30 frames per second that was the rule for film and TV until recently.
P
Since the transmission of TV has always and in all circumstances been based on a frequency of 50 or 60Hz, it was inevitable that capture and display technology would evolve to support progressive scan video at 50fps and 60fps ("Hz" is the number of frames a display can display, while 'fps' is the frame rate of a particular video stream). With the advent of high definition, these higher frame rates have become more common and are especially effective in sports. The fast-paced action of most sports matches is clearer, smoother and more detailed at 50/60 fps.
This is one of the main reasons why the latest generation of Apple TV 4K (2021) supports frame rates up to 60fps, ensuring that when viewing content from multiple streamers, you can enjoy sports or nature coverage with clean, smooth motion. So while HFR may have become a popular buzzword of late, we've really enjoyed great frame rate streams for years. And that doesn't stop at 50/60 fps, because as camera and display technologies have continued to develop, bandwidth has increased and compression algorithms have improved,
we're starting to see frame rates increase to 100/120fps.
There's been a lot of talk about 4K and HDR lately, and while the two innovations translate into a superior viewing experience, the addition of HFR could make the biggest difference when it comes to nature reporting or sports especially.

Will Smith in Gemini Man (Image credit: Paramount Pictures) In trying to reflect real life, the higher the resolution, the wider the active range and colors, and the higher the frame rate, the more realistic. it will be the experience.
Watching football, baseball, tennis, and athletics at higher frame rates will result in a more lifelike experience. You won't miss any of the action and everything will look silky smooth and detailed. The same goes for nature reports, where you will have the feeling that the tiger is in your living room! Interestingly, the one area in which HFR has failed to gain ground is film production and, by extension, series that frequently seek to mimic the aesthetic of feature films. There's a very distinctive look to 24fps, and as soon as the frame rate increases, the feeling of watching a movie is lost. Choosing 24 frames per second may have been a wise compromise a hundred years ago, but after a century of recording, it's the frame rate most people associate with motion picture film.
There is no technical restriction to record movies at higher frame rates, especially due to the fact that most productions are digital these days, and there have been some attempts to make movies on. HFR. Peter Jackson shot his Hobbit movies at 2fps and Ang Lee did two XNUMXfps movies (Billy Lynn's Long Halftime Walk and Gemini Man), but it's fair to say that neither of these productions were considered creative successes. The main criticisms these movies receive are that they look like ordinary "videos" or are "too realistic" and as a result, they lose that essential cinematic aesthetic. Therefore, while HFR will undoubtedly revolutionize reporting and sports coverage, it is unlikely to have an impact on the production of movies and series in the near future.
However, there is another medium where HFR will literally be a game changer.

(Image credit: Xbox Series X)
What does a great frame rate mean for games?
The evolution of game consoles has largely reflected the development of display technologies with resolutions that have moved from interlaced standard definition to progressive high definition and, more recently, to 4K at 50/60 fps. Anyone who regularly plays at frame rates higher than fifty / 60p is going to know that the experience is dramatically enhanced by the smooth and detailed movement.
While PC gamers have enjoyed HFR for some time, the arrival of the Xbox Series X and PS5 ushered in a new era of mass-market 100/120fps gaming.. While innovations like 4K, HDR, and ray tracing have their upsides, most gamers are going to name HFR as the biggest upgrade in next-gen console gaming, with its smooth motion and smooth, fluid gameplay.
How can I view HFR?
If you want to enjoy all the advantages of HFR,
you will need a television that uses a 100/120 Hz panel (depending on where you live) and have at least one HDMI 100 input so it can support 120/4 fps. sign. In terms of other hardware, the new Apple TV 50K can handle 60/2fps, as can many Ultra HD Blu-ray players (although there are very few 100fps discs outside of These 120 Movies and Lee), and the latest game consoles. it can manage playback at up to XNUMX/XNUMX fps.
There are multiple broadcasters and transmitters currently using 50/60 fps for sports coverage, multiple nature reports and YouTube videos, and there are already plans to increase the HFR to 100/120 fps in the near future.

 (Image credit: TechSmith
(Image credit: TechSmith
 Apple TV 4K (two thousand twenty-one) adds support for HFR display (Image credit: Apple)
Apple TV 4K (two thousand twenty-one) adds support for HFR display (Image credit: Apple)
 Will Smith in Gemini Man (Image credit: Paramount Pictures) In trying to reflect real life, the higher the resolution, the wider the active range and colors, and the higher the frame rate, the more realistic. it will be the experience. Watching football, baseball, tennis, and athletics at higher frame rates will result in a more lifelike experience. You won't miss any of the action and everything will look silky smooth and detailed. The same goes for nature reports, where you will have the feeling that the tiger is in your living room! Interestingly, the one area in which HFR has failed to gain ground is film production and, by extension, series that frequently seek to mimic the aesthetic of feature films. There's a very distinctive look to 24fps, and as soon as the frame rate increases, the feeling of watching a movie is lost. Choosing 24 frames per second may have been a wise compromise a hundred years ago, but after a century of recording, it's the frame rate most people associate with motion picture film.
There is no technical restriction to record movies at higher frame rates, especially due to the fact that most productions are digital these days, and there have been some attempts to make movies on. HFR. Peter Jackson shot his Hobbit movies at 2fps and Ang Lee did two XNUMXfps movies (Billy Lynn's Long Halftime Walk and Gemini Man), but it's fair to say that neither of these productions were considered creative successes. The main criticisms these movies receive are that they look like ordinary "videos" or are "too realistic" and as a result, they lose that essential cinematic aesthetic. Therefore, while HFR will undoubtedly revolutionize reporting and sports coverage, it is unlikely to have an impact on the production of movies and series in the near future. However, there is another medium where HFR will literally be a game changer.
Will Smith in Gemini Man (Image credit: Paramount Pictures) In trying to reflect real life, the higher the resolution, the wider the active range and colors, and the higher the frame rate, the more realistic. it will be the experience. Watching football, baseball, tennis, and athletics at higher frame rates will result in a more lifelike experience. You won't miss any of the action and everything will look silky smooth and detailed. The same goes for nature reports, where you will have the feeling that the tiger is in your living room! Interestingly, the one area in which HFR has failed to gain ground is film production and, by extension, series that frequently seek to mimic the aesthetic of feature films. There's a very distinctive look to 24fps, and as soon as the frame rate increases, the feeling of watching a movie is lost. Choosing 24 frames per second may have been a wise compromise a hundred years ago, but after a century of recording, it's the frame rate most people associate with motion picture film.
There is no technical restriction to record movies at higher frame rates, especially due to the fact that most productions are digital these days, and there have been some attempts to make movies on. HFR. Peter Jackson shot his Hobbit movies at 2fps and Ang Lee did two XNUMXfps movies (Billy Lynn's Long Halftime Walk and Gemini Man), but it's fair to say that neither of these productions were considered creative successes. The main criticisms these movies receive are that they look like ordinary "videos" or are "too realistic" and as a result, they lose that essential cinematic aesthetic. Therefore, while HFR will undoubtedly revolutionize reporting and sports coverage, it is unlikely to have an impact on the production of movies and series in the near future. However, there is another medium where HFR will literally be a game changer.
 (Image credit: Xbox Series X)
(Image credit: Xbox Series X)